
What is DIMM? Difference between DIMM and RAM?
A DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) is the physical memory stick that houses DRAM (Dynamic Random-Access Memory) chips. These chips serve as RAM, the volatile memory pool CPUs use to quickly access data during tasks.
Unlike storage devices such as SSDs or hard drives, RAM provides much faster data retrieval, directly impacting system responsiveness.
Key points about DIMMs and RAM:
- RAM is the memory chips on a DIMM. The RAM determines total memory capacity (e.g., “32GB of RAM per DIMM”).
- RAM is volatile, used for short-term computer memory. Data on RAM is lost when the system powers off
- More RAM = better multitasking since more data and applications can be stored in memory simultaneously. Data-intensive workloads can benefit from a lot of RAM since it reduces the latency when pulling data from storage drives. This includes real-time data analytics, CPU-only simulation, running calculations on large datasets.
- Insufficient RAM causes bottlenecks such as lag, freezing, and slow response times when handling demanding workloads.
Consumer vs. Enterprise DIMMs
- UDIMM (Unbuffered DIMM): Standard in desktops and laptops. Affordable, simple, and designed for everyday tasks like browsing, content consumption, and productivity.
- RDIMM & LRDIMM: Specialized modules designed for servers and enterprise workloads, offering higher capacity and stability. These will be the focus of this guide.
Differences between RDIMM and LRDIMM
| DIMM Type | Key Features | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| UDIMM |
|
|
| RDIMM |
|
|
| LRDIMM |
|
|
UDIMM – Unbuffered DIMM
Unbuffered DIMMs (UDIMMs) are the most common memory modules found in desktops, laptops, and entry-level systems. Unlike RDIMMs and LRDIMMs, they connect directly to the memory controller without a buffer, making them simpler and more affordable.
Key Features of UDIMMs
- Direct connection: No register or buffer, resulting in lower latency.
- Cost-effective: Widely available and inexpensive compared to enterprise DIMMs.
- Capacity limits: Support smaller memory sizes, making them unsuitable for large-scale workloads.
- ECC options: Typically non-ECC, though ECC UDIMMs exist for workstations and professional PCs.
Common Use Cases
- Consumer desktops and laptops for everyday computing.
- Workstations that don’t require massive memory scalability.
- General productivity, media consumption, and light multitasking.
RDIMM – Registered DIMM
Registered DIMMs (RDIMMs) are designed for greater stability and scalability than standard UDIMMs. They include a register buffer that improves signal integrity and reduces the electrical load on the memory controller. This makes them better suited for enterprise workloads.
Key Features of RDIMMs
- Buffered signals: A register sits between the DRAM modules and the memory controller, easing electrical load.
- Higher capacity: Supports more memory per system compared to UDIMMs.
- Data integrity: Available in ECC and non-ECC variants for reliability in mission-critical tasks.
- Latency trade-off: Slightly higher latency than UDIMMs due to the extra register.
Common Use Cases
- Servers and workstations running large datasets or complex applications.
- Virtualization environments where high memory capacity and reliability are essential.
- HPC clusters, scientific computing, and database servers.
LRDIMM – Load-Reduced DIMM
Load-Reduced DIMMs (LRDIMMs) push performance further by using advanced buffering to minimize electrical load and maximize capacity. They are built for systems that demand extreme memory density and efficiency.
Key Features of LRDIMMs
- Advanced buffering: Improves signal integrity and reduces electrical strain on the memory bus.
- Maximum capacity: Enables the highest memory density of any DIMM type.
- ECC support: Available with error correction for critical applications.
- Power efficiency: Buffering technology lowers power consumption compared to other high-capacity DIMMs.
Common Use Cases
- Enterprise-grade servers and data centers handling big data and virtualization at scale.
- Memory-heavy workloads such as in-memory databases and real-time analytics.
- Cloud computing platforms requiring high-density, reliable memory.
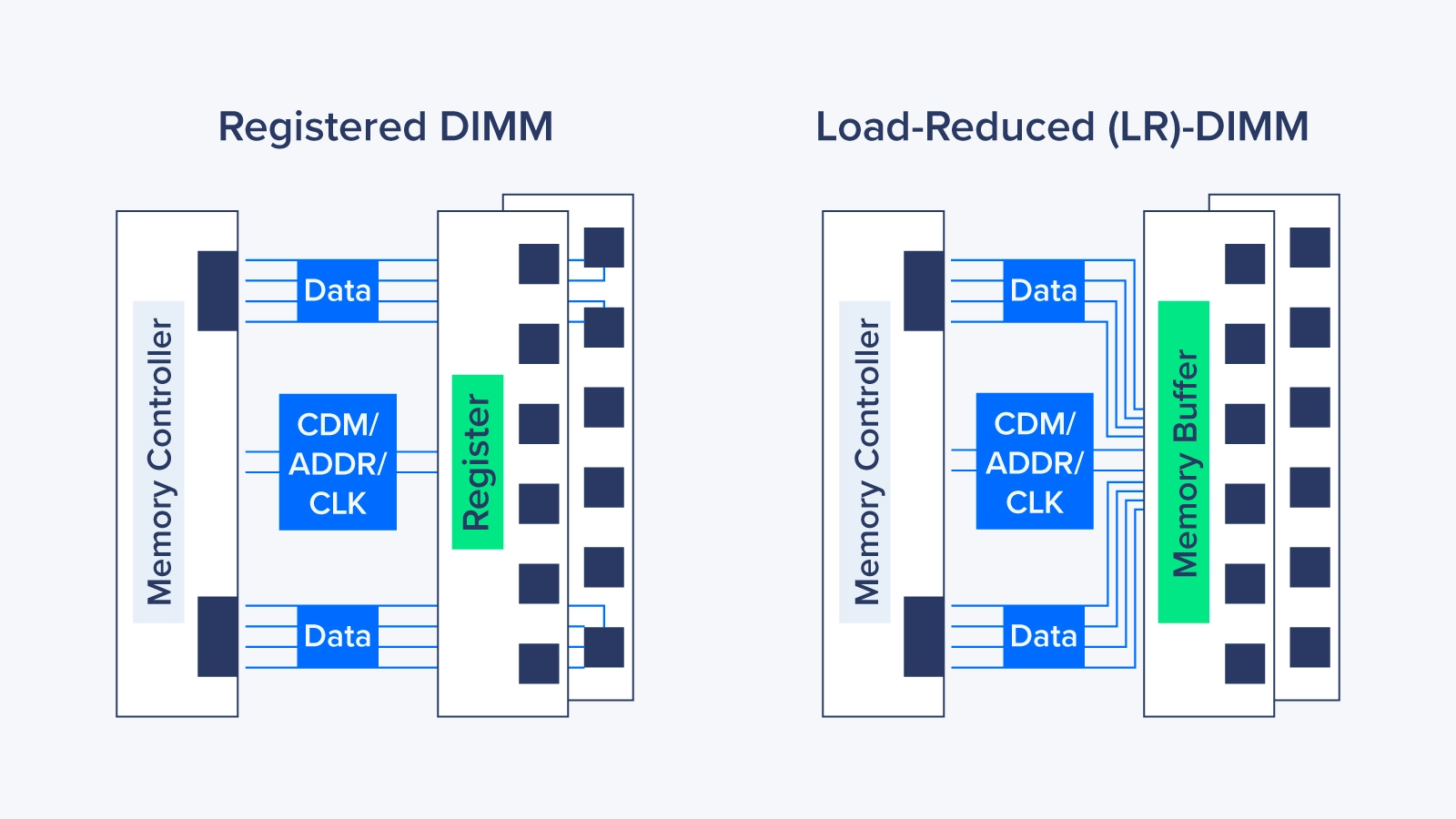
In LRDIMM, data must flow through the memory buffer first.
FAQs
What are the main differences between UDIMMs, RDIMMs, and LRDIMMs?
- UDIMMs: Unbuffered, affordable, and best for general computing.
- RDIMMs: Include a register for stability and scalability, ideal for servers and workstations.
- LRDIMMs: Use advanced buffering for maximum capacity, built for memory-intensive enterprise workloads.
Which type of DIMM is more reliable, ECC or non-ECC?
- ECC DIMMs detect and correct memory errors, making them essential for mission-critical applications.
- Non-ECC DIMMs are less expensive but lack error correction.
- Note: All DDR5 DIMMs include on-die ECC for internal error detection. However, true ECC DIMMs use sideband ECC, which remains the gold standard for reliability.
Can I mix different types of DIMMs in the same system?
Mixing UDIMMs, RDIMMs, and LRDIMMs is not recommended. It can cause compatibility problems and reduce performance. For best results, always use matching DIMMs from the same brand, speed, CAS latency, and more. These DIMMs should come as a set.
Are LRDIMMs backward compatible with older systems?
Not always. LRDIMMs require specific memory controllers that support load-reduced technology. Always confirm compatibility with your system specifications before upgrading.
Can I use LRDIMMs for gaming?
No. LRDIMMs are designed for enterprise workloads, not gaming. For gaming PCs, UDIMMs (standard RAM sticks) are the best option.
Are there performance differences between UDIMMs, RDIMMs, and LRDIMMs with the same specs?
Yes. LRDIMMs generally have slightly higher latency due to buffering. However, the real-world performance impact depends on the workload and system configuration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between UDIMMs, RDIMMs, and LRDIMMs is crucial when it comes to selecting the right memory modules for your computer system.
- UDIMMs offer a cost-effective solution for everyday computing
- RDIMMs provide increased stability and memory capacity for servers and workstations.
- LRDIMMs are the top choice for high-performance computing and memory-intensive tasks in enterprise environments.
When choosing the right DIMM type, consider your specific requirements, budget, and system compatibility. Whether you're workload is casual or professional, selecting the appropriate memory technology will optimize your system's performance.

Powering Workloads with Configurable Confidence
Power your workloads with confidence and configure an Exxact 2U TensorEX Server equipped with multiple GPUs, storage, networking, and more to build your ideal computing infrastructure.
Configure Now
Differences between Dual In-Line Memory Modules: RDIMM vs. LRDIMM
What is DIMM? Difference between DIMM and RAM?
A DIMM (Dual In-line Memory Module) is the physical memory stick that houses DRAM (Dynamic Random-Access Memory) chips. These chips serve as RAM, the volatile memory pool CPUs use to quickly access data during tasks.
Unlike storage devices such as SSDs or hard drives, RAM provides much faster data retrieval, directly impacting system responsiveness.
Key points about DIMMs and RAM:
- RAM is the memory chips on a DIMM. The RAM determines total memory capacity (e.g., “32GB of RAM per DIMM”).
- RAM is volatile, used for short-term computer memory. Data on RAM is lost when the system powers off
- More RAM = better multitasking since more data and applications can be stored in memory simultaneously. Data-intensive workloads can benefit from a lot of RAM since it reduces the latency when pulling data from storage drives. This includes real-time data analytics, CPU-only simulation, running calculations on large datasets.
- Insufficient RAM causes bottlenecks such as lag, freezing, and slow response times when handling demanding workloads.
Consumer vs. Enterprise DIMMs
- UDIMM (Unbuffered DIMM): Standard in desktops and laptops. Affordable, simple, and designed for everyday tasks like browsing, content consumption, and productivity.
- RDIMM & LRDIMM: Specialized modules designed for servers and enterprise workloads, offering higher capacity and stability. These will be the focus of this guide.
Differences between RDIMM and LRDIMM
| DIMM Type | Key Features | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| UDIMM |
|
|
| RDIMM |
|
|
| LRDIMM |
|
|
UDIMM – Unbuffered DIMM
Unbuffered DIMMs (UDIMMs) are the most common memory modules found in desktops, laptops, and entry-level systems. Unlike RDIMMs and LRDIMMs, they connect directly to the memory controller without a buffer, making them simpler and more affordable.
Key Features of UDIMMs
- Direct connection: No register or buffer, resulting in lower latency.
- Cost-effective: Widely available and inexpensive compared to enterprise DIMMs.
- Capacity limits: Support smaller memory sizes, making them unsuitable for large-scale workloads.
- ECC options: Typically non-ECC, though ECC UDIMMs exist for workstations and professional PCs.
Common Use Cases
- Consumer desktops and laptops for everyday computing.
- Workstations that don’t require massive memory scalability.
- General productivity, media consumption, and light multitasking.
RDIMM – Registered DIMM
Registered DIMMs (RDIMMs) are designed for greater stability and scalability than standard UDIMMs. They include a register buffer that improves signal integrity and reduces the electrical load on the memory controller. This makes them better suited for enterprise workloads.
Key Features of RDIMMs
- Buffered signals: A register sits between the DRAM modules and the memory controller, easing electrical load.
- Higher capacity: Supports more memory per system compared to UDIMMs.
- Data integrity: Available in ECC and non-ECC variants for reliability in mission-critical tasks.
- Latency trade-off: Slightly higher latency than UDIMMs due to the extra register.
Common Use Cases
- Servers and workstations running large datasets or complex applications.
- Virtualization environments where high memory capacity and reliability are essential.
- HPC clusters, scientific computing, and database servers.
LRDIMM – Load-Reduced DIMM
Load-Reduced DIMMs (LRDIMMs) push performance further by using advanced buffering to minimize electrical load and maximize capacity. They are built for systems that demand extreme memory density and efficiency.
Key Features of LRDIMMs
- Advanced buffering: Improves signal integrity and reduces electrical strain on the memory bus.
- Maximum capacity: Enables the highest memory density of any DIMM type.
- ECC support: Available with error correction for critical applications.
- Power efficiency: Buffering technology lowers power consumption compared to other high-capacity DIMMs.
Common Use Cases
- Enterprise-grade servers and data centers handling big data and virtualization at scale.
- Memory-heavy workloads such as in-memory databases and real-time analytics.
- Cloud computing platforms requiring high-density, reliable memory.

In LRDIMM, data must flow through the memory buffer first.
FAQs
What are the main differences between UDIMMs, RDIMMs, and LRDIMMs?
- UDIMMs: Unbuffered, affordable, and best for general computing.
- RDIMMs: Include a register for stability and scalability, ideal for servers and workstations.
- LRDIMMs: Use advanced buffering for maximum capacity, built for memory-intensive enterprise workloads.
Which type of DIMM is more reliable, ECC or non-ECC?
- ECC DIMMs detect and correct memory errors, making them essential for mission-critical applications.
- Non-ECC DIMMs are less expensive but lack error correction.
- Note: All DDR5 DIMMs include on-die ECC for internal error detection. However, true ECC DIMMs use sideband ECC, which remains the gold standard for reliability.
Can I mix different types of DIMMs in the same system?
Mixing UDIMMs, RDIMMs, and LRDIMMs is not recommended. It can cause compatibility problems and reduce performance. For best results, always use matching DIMMs from the same brand, speed, CAS latency, and more. These DIMMs should come as a set.
Are LRDIMMs backward compatible with older systems?
Not always. LRDIMMs require specific memory controllers that support load-reduced technology. Always confirm compatibility with your system specifications before upgrading.
Can I use LRDIMMs for gaming?
No. LRDIMMs are designed for enterprise workloads, not gaming. For gaming PCs, UDIMMs (standard RAM sticks) are the best option.
Are there performance differences between UDIMMs, RDIMMs, and LRDIMMs with the same specs?
Yes. LRDIMMs generally have slightly higher latency due to buffering. However, the real-world performance impact depends on the workload and system configuration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between UDIMMs, RDIMMs, and LRDIMMs is crucial when it comes to selecting the right memory modules for your computer system.
- UDIMMs offer a cost-effective solution for everyday computing
- RDIMMs provide increased stability and memory capacity for servers and workstations.
- LRDIMMs are the top choice for high-performance computing and memory-intensive tasks in enterprise environments.
When choosing the right DIMM type, consider your specific requirements, budget, and system compatibility. Whether you're workload is casual or professional, selecting the appropriate memory technology will optimize your system's performance.

Powering Workloads with Configurable Confidence
Power your workloads with confidence and configure an Exxact 2U TensorEX Server equipped with multiple GPUs, storage, networking, and more to build your ideal computing infrastructure.
Configure Now
