Introduction
Not every workload belongs in the cloud. Teams working on AI inference, simulation, or rendering often benefit from keeping compute local. When data sets are large, frequent, or sensitive, running jobs on-site avoids transfer delays, constant cloud access, and grants full hardware control.
GPU servers deliver strong acceleration for these tasks, and deploying them on-prem cuts recurring cloud costs. It also removes dependencies on shared infrastructure and lets teams operate without usage limits or contention.
Can I Deploy My GPU Servers in Non-Traditional Data Centers?
Yes! In fact, many businesses do not have dedicated data centers to house their server racks and GPU compute servers. Small businesses and labs don’t have a full-scale data center; they’re working with server rooms, closets, and converted spaces. You can support real GPU workloads as long as deployment is planned out thoughtfully.
- Power Draw: GPU servers draw a lot of power. In a small rack or closet, power outlets may not be accessible. For multi-GPU deployments, consider installing the closet with a three-phase 208V, or single-phase 240V receptacle.
- Space: Space is a big challenge, especially in rooms not purpose-built for rack deployment. Tight closets need careful planning for cable management and service access.
- Cooling: Ensuring peak performance requires efficient heat dissipation. If airflow is blocked or power delivery is uneven, thermal throttling or shutdowns follow. Solutions include AC systems and exhausting the closet.

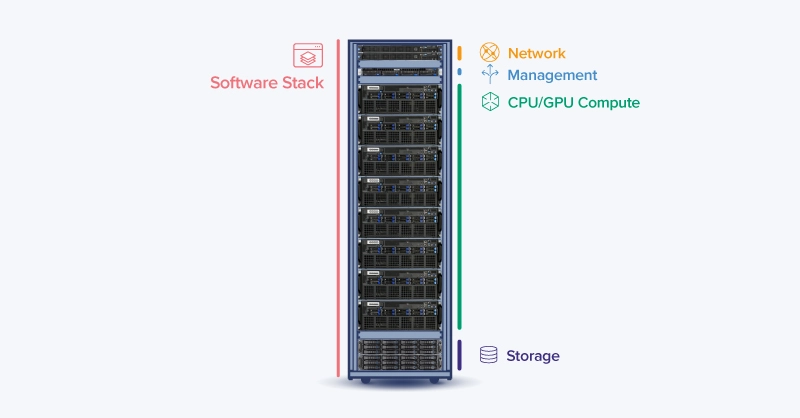
Hardware Selection for GPU Servers
Configure your deployment with GPUs that match your computing goals and fall within your thermal and power budget.
- Server Form Factor: If your server room or closet is limited in space, you can still deploy a substantial GPU system for powering your HPC workloads.
- If the room is shallow, consider short-depth rackmount servers
- Opt for rack mountable workstations. While they take up more rack units, they may have better airflow if not tightly packed together and are shorter in depth than standard servers
- GPU Choice: While flagship and top of the line cards have all the hype, GPUs down the stack can fit your space and power profile while delivering exceptional performance.
- If your workload needs extreme performance, stick with powerful cards like NVIDIA H200 NVL and RTX PRO 6000 Blackwell. Be prepared for their high power draw and cooling requirements.
- For distributed workloads, lower power cards can offer better parallelization.
- If airflow is limited in your server room, actively cooled GPUs can help dissipate heat versus passively cooled GPUs.
- You don’t need to populate all the slots. Fewer, high VRAM GPUs can promote better thermals than maxing out your slots.
- CPU and Memory: The CPU shouldn't bottleneck GPU throughput.
- Use CPUs with high PCIe lane count and enough cores to keep the pipeline full.
- Memory should match workload demands. AI training and simulation may need 128GB or more.
- Storage and Networking: Fast local storage avoids I/O stalls.
- NVMe SSDs over SATA wherever possible
- RAID is optional but useful for resilience
- Network ports at 10GbE minimum for shared workloads
- Consider direct-attach cables for short runs and fewer switches
With all these configuration decisions, making the right choices can get muddled. Our engineering team at Exxact will help you configure and plan the best solutions for your deployment needs and limitations.

Power Planning
For any HPC server deployment, you need stable, high-throughput power. Utilize Exxact’s BTU calculator when configuring your server and account for a 30% headroom.
- Circuit Requirements: GPU servers pull serious power, often more than what a standard outlet can safely supply.
- Prefer 208V circuits with 20A or 30A breakers
- Avoid running high-wattage servers on shared 15A/120V lines
- Check total draw, not just the GPU TDPs—fans, drives, and CPU add up
- Power Distribution: Use PDUs with clear metering. Inline monitoring helps spot overloaded branches before they trip as surge protectors to guard against brownouts
- Vertical PDUs save rack space
- Horizontal units work better in shallow racks
- If uptime is critical, use a double-conversion UPS for increased redundancy.
Managing and monitoring power and thermals is an essential part of data center IT. Utilize a cluster management tool like OpenHPC or TrinityX for monitoring and executing jobs via IPMI. Learn more about Exxact’s RackEXXpress for more information on how we support full-scale rack integration, including hardware, monitoring, and power management.
Cooling and Airflow
Heat builds up fast, especially in a confined space. High-performance GPUs generate hundreds of watts of thermal load each, and when you stack multiple cards into a chassis, the airflow path becomes critical. The room matters more than the server itself.
- Airflow Principles: Use equipment with front-to-back airflow and the hot air rises principle.
- Leave clearance behind the server for the exhaust
- Keep intake vents clean and unobstructed
- You can use a dual-vented door with the bottom as the intake and the top as the exhaust
- Closet-Specific Adjustments: Closets and converted rooms often lack ventilation.
- Add inline duct fans to pull warm air out
- Exhaust to the ceiling or an adjacent ventilated space
- Install a return vent if the room is sealed
- Noise, Safety, and Cost: Most servers aren’t quiet, and high electrical power can pose a fire hazard
- Acoustic-damping panels and flame-retardant lining the server room
- Run long workloads overnight to account for sustained noise and reduced energy costs
Running GPUs in a closet has been proven to work ,but not without planning. Temperature is the enemy of hardware and can reduce lifespan and increase crash risk. Cooling is, if not, the most important factor for deploying HPC hardware.
FAQ for Deploying GPU Servers in Non-Traditional Spaces
Can I run GPU servers in a small office or closet without a full data center?
Yes. With proper planning around power, cooling, and space, high-performance GPU systems can operate reliably in small data centers, small rooms, and even closets.
What kind of power setup do I need for running high-performance GPU systems on-prem?
Use 208V circuits with 20A or 30A breakers. Avoid standard 120V office outlets for multi-GPU servers. Metered PDUs (power distribution units), UPSs (uninterrupted power supplies), and surge protection are essential.
Can I use residential power circuits for enterprise-grade servers?
Single-GPU workstations may work on a 15A or 20A 120V line, but multi-GPU workstations or rackmount servers will exceed that draw under load. Don’t run them on shared residential circuits.
What kind of remote management tools should I include in a small-scale deployment?
Look for servers with IPMI or BMC support and manage them through software like OpenHPC or TrinityX. These let you power cycle, monitor temps, and update firmware remotely without having to physically service the system in the closet. Contact Exxact to learn more.
How do I decide which GPUs to use for my deployment?
Start with your workload. Once you evaluate your workload performance necessities, balance it with space, thermals, and available power. For CFD and simulation, use GPUs with strong FP64 like the H200 NVL. For rendering and visualization, use GPUs with video encode and decode like RTX PRO 6000 Blackwell. For parallelizable low intensity workloads, use multiple middle-tier GPUs like RTX 4500 Ada.
Conclusion & TLDR
GPU servers don’t need a full data center. If the workload demands power and control, a closet or small equipment room can work with appropriate planning.
Pick the right enclosure and rack. Know your power limits or install 208V receptacles. Ensure proper airflow for cooling. Plan remote management and networking to simplify your server setup.
AI prototyping and deployment, engineering simulation teams, and life science research labs can run real GPU infrastructure on-site with the right build. If you need help designing a system for your space and workloads, Exxact will help guide you through the configuration, build, delivery, and deployment process.

Fueling Innovation with an Exxact Multi-GPU Server
Accelerate your workload exponentially with the right system optimized to your use case. Exxact 4U Servers are not just a high-performance computer; it is the tool for propelling your innovation to new heights.
Configure Now
Deploying GPU Servers On-Prem in Non-Traditional Data Centers
Introduction
Not every workload belongs in the cloud. Teams working on AI inference, simulation, or rendering often benefit from keeping compute local. When data sets are large, frequent, or sensitive, running jobs on-site avoids transfer delays, constant cloud access, and grants full hardware control.
GPU servers deliver strong acceleration for these tasks, and deploying them on-prem cuts recurring cloud costs. It also removes dependencies on shared infrastructure and lets teams operate without usage limits or contention.
Can I Deploy My GPU Servers in Non-Traditional Data Centers?
Yes! In fact, many businesses do not have dedicated data centers to house their server racks and GPU compute servers. Small businesses and labs don’t have a full-scale data center; they’re working with server rooms, closets, and converted spaces. You can support real GPU workloads as long as deployment is planned out thoughtfully.
- Power Draw: GPU servers draw a lot of power. In a small rack or closet, power outlets may not be accessible. For multi-GPU deployments, consider installing the closet with a three-phase 208V, or single-phase 240V receptacle.
- Space: Space is a big challenge, especially in rooms not purpose-built for rack deployment. Tight closets need careful planning for cable management and service access.
- Cooling: Ensuring peak performance requires efficient heat dissipation. If airflow is blocked or power delivery is uneven, thermal throttling or shutdowns follow. Solutions include AC systems and exhausting the closet.

Hardware Selection for GPU Servers
Configure your deployment with GPUs that match your computing goals and fall within your thermal and power budget.
- Server Form Factor: If your server room or closet is limited in space, you can still deploy a substantial GPU system for powering your HPC workloads.
- If the room is shallow, consider short-depth rackmount servers
- Opt for rack mountable workstations. While they take up more rack units, they may have better airflow if not tightly packed together and are shorter in depth than standard servers
- GPU Choice: While flagship and top of the line cards have all the hype, GPUs down the stack can fit your space and power profile while delivering exceptional performance.
- If your workload needs extreme performance, stick with powerful cards like NVIDIA H200 NVL and RTX PRO 6000 Blackwell. Be prepared for their high power draw and cooling requirements.
- For distributed workloads, lower power cards can offer better parallelization.
- If airflow is limited in your server room, actively cooled GPUs can help dissipate heat versus passively cooled GPUs.
- You don’t need to populate all the slots. Fewer, high VRAM GPUs can promote better thermals than maxing out your slots.
- CPU and Memory: The CPU shouldn't bottleneck GPU throughput.
- Use CPUs with high PCIe lane count and enough cores to keep the pipeline full.
- Memory should match workload demands. AI training and simulation may need 128GB or more.
- Storage and Networking: Fast local storage avoids I/O stalls.
- NVMe SSDs over SATA wherever possible
- RAID is optional but useful for resilience
- Network ports at 10GbE minimum for shared workloads
- Consider direct-attach cables for short runs and fewer switches
With all these configuration decisions, making the right choices can get muddled. Our engineering team at Exxact will help you configure and plan the best solutions for your deployment needs and limitations.

Power Planning
For any HPC server deployment, you need stable, high-throughput power. Utilize Exxact’s BTU calculator when configuring your server and account for a 30% headroom.
- Circuit Requirements: GPU servers pull serious power, often more than what a standard outlet can safely supply.
- Prefer 208V circuits with 20A or 30A breakers
- Avoid running high-wattage servers on shared 15A/120V lines
- Check total draw, not just the GPU TDPs—fans, drives, and CPU add up
- Power Distribution: Use PDUs with clear metering. Inline monitoring helps spot overloaded branches before they trip as surge protectors to guard against brownouts
- Vertical PDUs save rack space
- Horizontal units work better in shallow racks
- If uptime is critical, use a double-conversion UPS for increased redundancy.
Managing and monitoring power and thermals is an essential part of data center IT. Utilize a cluster management tool like OpenHPC or TrinityX for monitoring and executing jobs via IPMI. Learn more about Exxact’s RackEXXpress for more information on how we support full-scale rack integration, including hardware, monitoring, and power management.

Cooling and Airflow
Heat builds up fast, especially in a confined space. High-performance GPUs generate hundreds of watts of thermal load each, and when you stack multiple cards into a chassis, the airflow path becomes critical. The room matters more than the server itself.
- Airflow Principles: Use equipment with front-to-back airflow and the hot air rises principle.
- Leave clearance behind the server for the exhaust
- Keep intake vents clean and unobstructed
- You can use a dual-vented door with the bottom as the intake and the top as the exhaust
- Closet-Specific Adjustments: Closets and converted rooms often lack ventilation.
- Add inline duct fans to pull warm air out
- Exhaust to the ceiling or an adjacent ventilated space
- Install a return vent if the room is sealed
- Noise, Safety, and Cost: Most servers aren’t quiet, and high electrical power can pose a fire hazard
- Acoustic-damping panels and flame-retardant lining the server room
- Run long workloads overnight to account for sustained noise and reduced energy costs
Running GPUs in a closet has been proven to work ,but not without planning. Temperature is the enemy of hardware and can reduce lifespan and increase crash risk. Cooling is, if not, the most important factor for deploying HPC hardware.
FAQ for Deploying GPU Servers in Non-Traditional Spaces
Can I run GPU servers in a small office or closet without a full data center?
Yes. With proper planning around power, cooling, and space, high-performance GPU systems can operate reliably in small data centers, small rooms, and even closets.
What kind of power setup do I need for running high-performance GPU systems on-prem?
Use 208V circuits with 20A or 30A breakers. Avoid standard 120V office outlets for multi-GPU servers. Metered PDUs (power distribution units), UPSs (uninterrupted power supplies), and surge protection are essential.
Can I use residential power circuits for enterprise-grade servers?
Single-GPU workstations may work on a 15A or 20A 120V line, but multi-GPU workstations or rackmount servers will exceed that draw under load. Don’t run them on shared residential circuits.
What kind of remote management tools should I include in a small-scale deployment?
Look for servers with IPMI or BMC support and manage them through software like OpenHPC or TrinityX. These let you power cycle, monitor temps, and update firmware remotely without having to physically service the system in the closet. Contact Exxact to learn more.
How do I decide which GPUs to use for my deployment?
Start with your workload. Once you evaluate your workload performance necessities, balance it with space, thermals, and available power. For CFD and simulation, use GPUs with strong FP64 like the H200 NVL. For rendering and visualization, use GPUs with video encode and decode like RTX PRO 6000 Blackwell. For parallelizable low intensity workloads, use multiple middle-tier GPUs like RTX 4500 Ada.
Conclusion & TLDR
GPU servers don’t need a full data center. If the workload demands power and control, a closet or small equipment room can work with appropriate planning.
Pick the right enclosure and rack. Know your power limits or install 208V receptacles. Ensure proper airflow for cooling. Plan remote management and networking to simplify your server setup.
AI prototyping and deployment, engineering simulation teams, and life science research labs can run real GPU infrastructure on-site with the right build. If you need help designing a system for your space and workloads, Exxact will help guide you through the configuration, build, delivery, and deployment process.

Fueling Innovation with an Exxact Multi-GPU Server
Accelerate your workload exponentially with the right system optimized to your use case. Exxact 4U Servers are not just a high-performance computer; it is the tool for propelling your innovation to new heights.
Configure Now
