
Introduction
Traditional PCIe NICs have served this role well for years, offering a proven approach to server networking. Modern servers require faster and more reliable network connections to support data-intensive workloads. As data traffic grows and applications continue to require lower latency, traditional networking options can fall short in flexibility, scalability, and performance.
OCP 3.0 was developed to address some of the limitations PCIe NICs face in dense, high-performance environments. It introduces a standardized design that improves airflow, simplifies serviceability, and supports the bandwidth requirements of modern data centers.
What is OCP 3.0 for Networking?
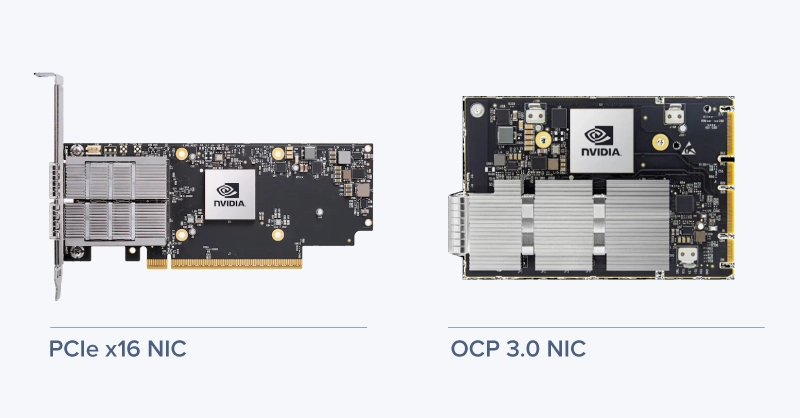
OCP NIC 3.0 is a dedicated mezzanine form factor for network interface cards developed by the Open Compute Project, created to improve interoperability and address challenges in traditional NIC designs. OCP NIC 3.0 modules are slim, hot-swappable cards mounted via the front or rear of a server, making them easier to access and replace.
This hot-swapping design also reduces downtime during maintenance, improves airflow in densely packed racks, helping servers maintain thermal efficiency. With support for speeds up to 400GbE, OCP 3.0 NICs meet the needs of modern workloads such as AI training, cloud computing, and edge deployments.
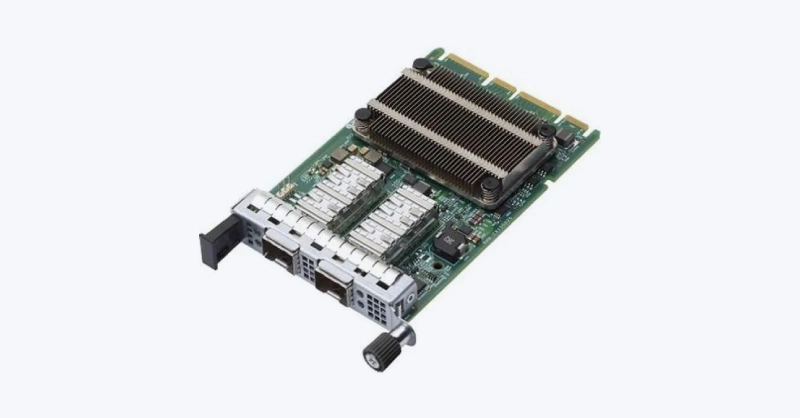

Advantages of OCP 3.0 NICs
OCP NIC 3.0 introduces a design built for the needs of modern servers. Its standardized approach delivers several key benefits:
- Serviceability: Front-access installation makes it easy to swap NICs without opening the chassis or shutting down the system.
- Improved airflow: The mezzanine-style layout allows airflow to move cleanly through the server, helping maintain thermal efficiency in dense racks.
- Space efficiency: By moving networking outside traditional PCIe slots, servers free up room for GPUs, storage devices, and accelerators.
- High-speed support: OCP 3.0 NICs handle speeds from 25GbE to 400GbE, addressing the growing bandwidth needs of data center workloads.
OCP 3.0 Form Factors and Connectors
OCP NIC 3.0 cards are available in multiple form factors and connector types:
- SFF (Small Form Factor): Compact size for space-constrained servers. This is the standard OCP 3.0 slot type with up to x16 PCIe lanes.
- TSFF (Tall Small Form Factor): Same dimensions as SFF but with taller clearance for larger heatsinks
- LFF (Large Form Factor): Wider form factor that requires an additional OCP port. Wider heatsinks allow for higher speed NICs to dissipate heat. The additional port also enables up to 32x PCIe lanes. This form factor is less common.
The connectors used in OCP NIC 3.0 determine how much PCIe bandwidth the NIC can deliver:
- 2C Connector: Supports up to 8 lanes of PCIe (x8). Typically used for NICs with speeds up to 100GbE.
- 4C Connector: Supports up to 16 lanes of PCIe (x16). Required for NICs running at 200GbE and 400GbE, where higher bandwidth and throughput are critical.
These options allow server designers to match the right OCP NIC to their networking requirements without sacrificing thermal or mechanical efficiency.
OCP 3.0 NICs vs Traditional PCIe NICs
Both OCP 3.0 NICs and PCIe NICs provide high-speed network connectivity, but their designs target different priorities in server architecture.
Traditional PCIe NICs:
- Use standard PCIe slots in the server motherboard.
- Offer excellent performance and compatibility across a wide range of systems, including workstations.
- Require access to the server interior for installation and replacement, which can interrupt workflows in live environments.
OCP 3.0 NICs:
- Hot-swappable networking port to a front or rear accessible mezzanine slot.
- Simplify maintenance with hot-swap capability, avoiding server downtime
- Improve airflow in dense rack environments and free up PCIe slots for other expansion cards.
- Support higher port densities and speeds with options like 200GbE and 400GbE.
OCP NIC 3.0 does not replace PCIe NICs outright. Instead, it addresses specific challenges in hyperscale and enterprise data centers where serviceability, thermal efficiency, and high bandwidth are critical.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does OCP NIC 3.0 differ from traditional PCIe NICs?
OCP NIC 3.0 moves network cards to a front or rear access hot-swappable mezzanine slot for better flexibility and serviceability. It frees PCIe slots for other uses and supports very high-speed connections. PCIe NICs remain widely compatible and reliable, but require internal access for installation.
What types of network speeds do OCP 3.0 NICs support?
OCP NIC 3.0 supports speeds ranging from 25GbE up to 400GbE. The standard offers two connector types: 2C with 8 PCIe lanes (x8) and 4C with 16 PCIe lanes (x16). The number of PCIe lanes determines the maximum data transfer rate the card can support, varying by the manufacturers of the networking card.
Can OCP NIC 3.0 cards be hot-swapped during server operation?
Yes. One of the main advantages of OCP NIC 3.0 is that cards can be replaced or installed without shutting down the server, reducing downtime and simplifying maintenance.
Are OCP NIC 3.0 cards compatible with all server models?
No. OCP NIC 3.0 requires servers designed with compatible mezzanine slots. Many server platforms support it, but not all. Be sure to ask our engineers about OCP 3.0 compatible platforms!
Is OCP NIC 3.0 suitable for all data center sizes, or only large-scale deployments?
OCP NIC 3.0 is mainly designed for hyperscale and enterprise data centers where high bandwidth, serviceability, and airflow are critical. Smaller data centers can benefit but may find traditional PCIe NICs more practical due to lower complexity.
Conclusion
OCP NIC 3.0 offers a focused solution for the demands of modern data centers. Its design improves serviceability, airflow, and space efficiency while supporting very high network speeds. Traditional PCIe NICs remain reliable and widely used, but OCP 3.0 fills a niche where quick maintenance and thermal management are critical.
For organizations managing large-scale or high-density server deployments, adopting OCP NIC 3.0 can reduce downtime and improve overall network performance. The standard’s flexibility with form factors and connectors makes it easy to match the right NIC to specific workload needs.
Looking to configure a high-performance server or expand upon your existing computing infrastructure? Exxact builds configurable workstations, servers, and full clusters to address your computing challenges. Talk to us today about your computing requirements, necessities today.

Fueling Innovation with an Exxact Multi-GPU Server
Accelerate your workload exponentially with the right system optimized to your use case. Exxact 4U Servers are not just a high-performance computer; it is the tool for propelling your innovation to new heights.
Configure Now
What are OCP 3.0 NICs?
Introduction
Traditional PCIe NICs have served this role well for years, offering a proven approach to server networking. Modern servers require faster and more reliable network connections to support data-intensive workloads. As data traffic grows and applications continue to require lower latency, traditional networking options can fall short in flexibility, scalability, and performance.
OCP 3.0 was developed to address some of the limitations PCIe NICs face in dense, high-performance environments. It introduces a standardized design that improves airflow, simplifies serviceability, and supports the bandwidth requirements of modern data centers.
What is OCP 3.0 for Networking?
OCP NIC 3.0 is a dedicated mezzanine form factor for network interface cards developed by the Open Compute Project, created to improve interoperability and address challenges in traditional NIC designs. OCP NIC 3.0 modules are slim, hot-swappable cards mounted via the front or rear of a server, making them easier to access and replace.
This hot-swapping design also reduces downtime during maintenance, improves airflow in densely packed racks, helping servers maintain thermal efficiency. With support for speeds up to 400GbE, OCP 3.0 NICs meet the needs of modern workloads such as AI training, cloud computing, and edge deployments.

Advantages of OCP 3.0 NICs
OCP NIC 3.0 introduces a design built for the needs of modern servers. Its standardized approach delivers several key benefits:
- Serviceability: Front-access installation makes it easy to swap NICs without opening the chassis or shutting down the system.
- Improved airflow: The mezzanine-style layout allows airflow to move cleanly through the server, helping maintain thermal efficiency in dense racks.
- Space efficiency: By moving networking outside traditional PCIe slots, servers free up room for GPUs, storage devices, and accelerators.
- High-speed support: OCP 3.0 NICs handle speeds from 25GbE to 400GbE, addressing the growing bandwidth needs of data center workloads.
OCP 3.0 Form Factors and Connectors
OCP NIC 3.0 cards are available in multiple form factors and connector types:
- SFF (Small Form Factor): Compact size for space-constrained servers. This is the standard OCP 3.0 slot type with up to x16 PCIe lanes.
- TSFF (Tall Small Form Factor): Same dimensions as SFF but with taller clearance for larger heatsinks
- LFF (Large Form Factor): Wider form factor that requires an additional OCP port. Wider heatsinks allow for higher speed NICs to dissipate heat. The additional port also enables up to 32x PCIe lanes. This form factor is less common.
The connectors used in OCP NIC 3.0 determine how much PCIe bandwidth the NIC can deliver:
- 2C Connector: Supports up to 8 lanes of PCIe (x8). Typically used for NICs with speeds up to 100GbE.
- 4C Connector: Supports up to 16 lanes of PCIe (x16). Required for NICs running at 200GbE and 400GbE, where higher bandwidth and throughput are critical.
These options allow server designers to match the right OCP NIC to their networking requirements without sacrificing thermal or mechanical efficiency.
OCP 3.0 NICs vs Traditional PCIe NICs
Both OCP 3.0 NICs and PCIe NICs provide high-speed network connectivity, but their designs target different priorities in server architecture.
Traditional PCIe NICs:
- Use standard PCIe slots in the server motherboard.
- Offer excellent performance and compatibility across a wide range of systems, including workstations.
- Require access to the server interior for installation and replacement, which can interrupt workflows in live environments.
OCP 3.0 NICs:
- Hot-swappable networking port to a front or rear accessible mezzanine slot.
- Simplify maintenance with hot-swap capability, avoiding server downtime
- Improve airflow in dense rack environments and free up PCIe slots for other expansion cards.
- Support higher port densities and speeds with options like 200GbE and 400GbE.
OCP NIC 3.0 does not replace PCIe NICs outright. Instead, it addresses specific challenges in hyperscale and enterprise data centers where serviceability, thermal efficiency, and high bandwidth are critical.

Frequently Asked Questions
How does OCP NIC 3.0 differ from traditional PCIe NICs?
OCP NIC 3.0 moves network cards to a front or rear access hot-swappable mezzanine slot for better flexibility and serviceability. It frees PCIe slots for other uses and supports very high-speed connections. PCIe NICs remain widely compatible and reliable, but require internal access for installation.
What types of network speeds do OCP 3.0 NICs support?
OCP NIC 3.0 supports speeds ranging from 25GbE up to 400GbE. The standard offers two connector types: 2C with 8 PCIe lanes (x8) and 4C with 16 PCIe lanes (x16). The number of PCIe lanes determines the maximum data transfer rate the card can support, varying by the manufacturers of the networking card.
Can OCP NIC 3.0 cards be hot-swapped during server operation?
Yes. One of the main advantages of OCP NIC 3.0 is that cards can be replaced or installed without shutting down the server, reducing downtime and simplifying maintenance.
Are OCP NIC 3.0 cards compatible with all server models?
No. OCP NIC 3.0 requires servers designed with compatible mezzanine slots. Many server platforms support it, but not all. Be sure to ask our engineers about OCP 3.0 compatible platforms!
Is OCP NIC 3.0 suitable for all data center sizes, or only large-scale deployments?
OCP NIC 3.0 is mainly designed for hyperscale and enterprise data centers where high bandwidth, serviceability, and airflow are critical. Smaller data centers can benefit but may find traditional PCIe NICs more practical due to lower complexity.
Conclusion
OCP NIC 3.0 offers a focused solution for the demands of modern data centers. Its design improves serviceability, airflow, and space efficiency while supporting very high network speeds. Traditional PCIe NICs remain reliable and widely used, but OCP 3.0 fills a niche where quick maintenance and thermal management are critical.
For organizations managing large-scale or high-density server deployments, adopting OCP NIC 3.0 can reduce downtime and improve overall network performance. The standard’s flexibility with form factors and connectors makes it easy to match the right NIC to specific workload needs.
Looking to configure a high-performance server or expand upon your existing computing infrastructure? Exxact builds configurable workstations, servers, and full clusters to address your computing challenges. Talk to us today about your computing requirements, necessities today.

Fueling Innovation with an Exxact Multi-GPU Server
Accelerate your workload exponentially with the right system optimized to your use case. Exxact 4U Servers are not just a high-performance computer; it is the tool for propelling your innovation to new heights.
Configure Now
