Are you looking into an HPC workstation or server for your workloads to reduce the time to completion? Should you spring for a Dual CPU configuration for more performance? We want to flush out any details on considering dual CPUs and highlight what are the advantages and considerations of a Dual CPU system versus a Single CPU.
What do you get with Dual CPU system?
Dual CPU systems require dedicated motherboards that enable the installation of two CPUs. And yes, the CPUs must be identical, otherwise your system will not boot. Do not mix and match processors or you risk damage to your system.
Ideally, a dual CPU platform will offer twice the memory slots, two independent sets of cache, and more PCIe lanes connected for more graphics cards or other expansion cards, as well as support for more storage. However, with the size of processors getting larger and larger versus a standard motherboard size, there can be concessions made in I/O depending on the chassis.
The point of a dual CPU setup is not only to increase the number of ports and I/O but also to double the number of cores and separate processing power for better memory bandwidth, parallel performance, and improved multitasking. Workloads such as rendering complex 3D scenes, exporting large video files, deploying multi-instance virtual machines, training complex AI, and more can take advantage of more computing and more cores.
Dual CPU systems can deliver performance uplift over single CPU systems by sharing memory resources and splitting workloads between the two. Doubling the number of processors should effectively double the performance of a workload, right? So why isn’t everyone running a dual CPU configuration?
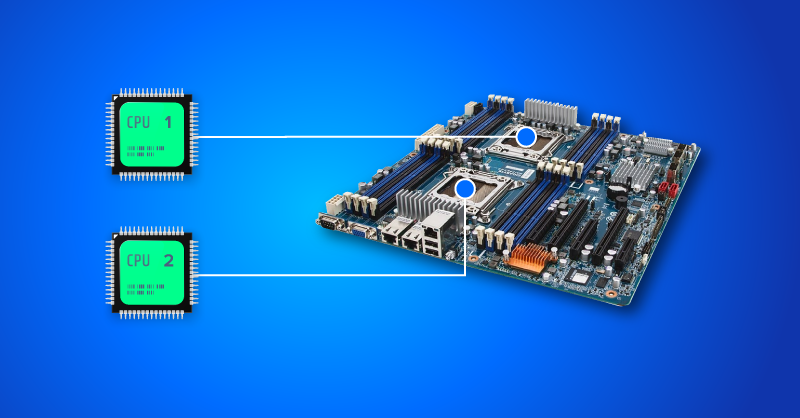
Does Your Workload Require 2 CPUs?
Many common workloads that day-to-day people do, like gaming, surfing the web, streaming movies, or graphic design and content creation often don’t need anything more than a single CPU. Most casual workloads cannot even take advantage of the second CPU and will actually suffer in performance. CPU 2 stands idle, consuming wattage and generating heat without doing any work, not to mention the extra cost incurred.
With the technological advances in GPU optimization and single socket CPUs like AMD Threadripper PRO and Intel Xeon W, compute intensive tasks can reach optimal performance without a second CPU counterpart. Taking GPUs out of the equation, modern CPUs now have higher core counts, thread count, cache, and computing power than ever before, replacing the dual CPU setup for a more economical single CPU configuration.
Another factor to consider is the intercommunication between two CPUs. If your workload does reach high throughput, bear in mind dual CPU servers have additional latency due to NUMA (non-uniform memory access) where the two CPUs have to communicate to share resources. NUMA is not a bottleneck, it is just the inherent design of incorporating the large number of cores across two processors. NUMA is actually quite efficient in solving this issue when sharing CPU1's share of the workload with CPU2's. However, if you can avoid the NUMA overhead, you can mitigate the latency by partitioning workloads between the two CPUs. NUMA isn't a drawback or disadvantage, just a consideration/precaution.
It is also important to consider the if dual CPU computing is supported and optimized by that workload. Some workloads won't recognize the second CPU as available resources.
If you are choosing between dual 32 core CPUs or a single 64 core CPU, it is best to stick with the single CPU configuration to avoid the dual CPU communication overhead and unknown optimization, especially when your workload isn’t partitioning compute like in virtualization and powering cloud instances.

Fueling Innovation with an Exxact Multi-GPU Server
Accelerate your workload exponentially with the right system optimized to your use case. Exxact 4U Servers are not just a high-performance computer; it is the tool for propelling your innovation to new heights.
Configure NowWhen are Dual CPU Systems Used?
As of 2024, present-day CPUs are miles ahead of what they used to be; high core counts, multi-thread capabilities, and high performance; dual CPUs are rarely at your desk, only seen in data centers.
For example, let's look at streaming games online, where a dual CPUs setup could be beneficial in theory. The gaming workload and the video/streaming workload can be partitioning between two CPUs to avoid using important computing resources for both the gameplay and the recording thus providing a higher quality stream. However, instead of investing in a dual CPU motherboard and workstation, this workload often uses a setup with two single CPU systems. The added flexibility for hardware such as dedicated beefy GPU for one system and storage controller and capture card for stream recordings in the other. Having space for each component is more important than its density here.
True dual CPU systems are reserved for HPC servers designed for the smallest footprint. A large data center infrastructure would house thousands of servers executing high-performance tasks. Deploying 5,000 machines as opposed to 10,000 can save on rack space and time spent servicing these machines.
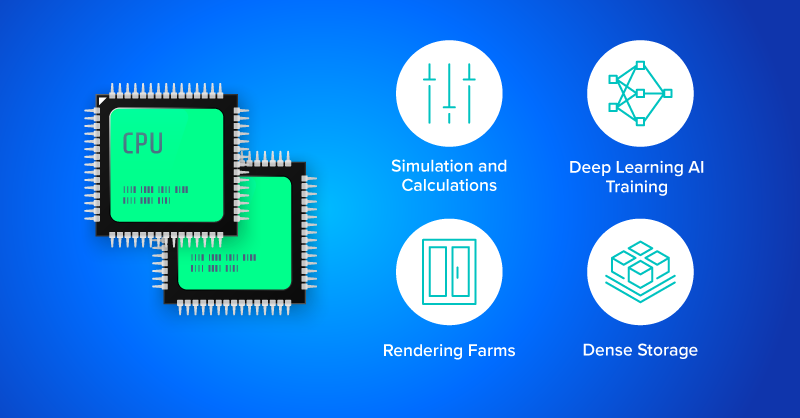
Some use cases for dual CPU systems include:
- Scientific Simulation
- Rendering Farms for large video and 3D content
- Deep Learning AI Training & Inference
- Computer Aided Engineering (CAE)
- Finite Element Method/Analysis (FEM/FEA)
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
- Dense Storage
- Virtualization Environments
The advantage of a dual CPU system is performance density. Multi-threaded CPU-intensive applications can be executed in a breeze, even handling multiple high-capacity databases due to their sheer power. The 64-core 128-thread AMD EPYC is a multi-threaded performance king; with 2 of them in one system, their computing power is no joke.
Furthermore, data centers optimize these CPUs to perform a set of tasks at extremely high speeds with no CPU utilization wasted. For a system that fits in a single rack at the data center, nothing beats a dual CPU system that can be virtualized into two systems. These dual CPU systems effectively have two enterprise-grade single CPU systems populating only a single rack space in the data center crunching huge amounts of data and need any last drop of extreme performance they can get within a small footprint.
Dual CPU systems also enable more PCIe lanes for multiple GPUs useful for operation doing AI training, building complex algorithms, or molecular dynamics. By increasing your CPU count and PCIe lanes, you can double your GPU count and cut time spent training or running simulations.
Some workloads within the ones listed however, sometimes cannot take advantage of a dual CPU setup, or is not CPU dependent, relying on mostly the GPU. Life Science simulation programs like AMBER and GROMACS actual lose performance when ran on a dual CPU configuration and would be better off with a single processor.
Dual CPU workstation also exist. However, the space required to fit 2 modern CPUs (especially the extra-large AMD EPYC 9004) on a standard ATX or EATX motherboard can get cramped. Stuffing compute in a less dense chassis can leave additional PCIe lanes unaccounted, incur RAM limitations, and reduce number of storage bays. Dual CPU workstations are reserved for those looking for more CPU compute in a flexible workstation form factor.
How to Optimize Dual CPU System Workloads
The biggest factor when deciding on a dual CPU or single CPU solution is the workload. While Dual CPU systems can be beneficial for parallel computing (calculations performed simultaneously) like rendering, they can cause latency issues when executing tasks serially (calculations performed subsequently). While a Cinebench test (parallel) can show double the performance, a 7zip test (serial) won’t be able to take advantage of dual CPU and in some faults, be slower.
The best way to optimize dual CPUs is to separate datasets and workloads. When training a deep learning neural network for Natural Language Processing, split the preprocessing and the and training tasks to utilize both CPUs effectively. Or for your scientific research in cryo-EM 2D classification and 3D reconstruction allocate resources to the 2D classification while the rest are allocated for 3D reconstruction. Almost any HPC application can be sped up dramatically if you can parallelize the steps in a workload since the time it takes to complete 2 conjoining tasks can be faster than sequentially executing them.
Deploying a virtual machine using a hypervisor like VirtualBox or RedHat can make two separate systems for two separate purposes. Run the two datasets separately on the two VMs. Because VM1 and VM2 are independent machines operating like a single CPU system, these CPUs can work in parallel executing serial tasks.
Some research institutes will opt to configure a whole cluster and partition resources to specific steps in the research. Some compute for the molecular dynamics simulation, some for the cryo-EM machine in the lab, some for protein folding to conceptualize binding targets, you get the idea. By splitting the resources up among lower computationally expensive workloads enable efficient and consolidated workflow where all the working data is in a single place. Reducing the time to transfer data from workstation to workstation, keeping data stored in the cluster, and computing everything in parallel dramatically accelerates research and reduced the total time to completion.
So, do you need Dual CPUs?
With current-generation CPUs holding so much power, there isn’t a substantial need for a dual CPU system for mainstream consumer usage. Enthusiast AI training and deep learning workloads can benefit from parallel computing through a single CPU with multiple GPUs.
However, if your workload is on the HPC level like crunching extremely large datasets, training large AI models with the highest efficiency, or running massively compute-intensive scientific simulations, and you want to execute these tasks with the smallest footprint, deploying multiple Dual CPU configuration might be your answer.

We're Here to Deliver the Tools to Power Your Research
With access to the highest performing hardware, at Exxact, we can offer the platform optimized for your deployment, budget, and desired performance so you can make an impact with your research!
Talk to an Engineer Today
Do I Need 2 CPUs?
Are you looking into an HPC workstation or server for your workloads to reduce the time to completion? Should you spring for a Dual CPU configuration for more performance? We want to flush out any details on considering dual CPUs and highlight what are the advantages and considerations of a Dual CPU system versus a Single CPU.
What do you get with Dual CPU system?
Dual CPU systems require dedicated motherboards that enable the installation of two CPUs. And yes, the CPUs must be identical, otherwise your system will not boot. Do not mix and match processors or you risk damage to your system.
Ideally, a dual CPU platform will offer twice the memory slots, two independent sets of cache, and more PCIe lanes connected for more graphics cards or other expansion cards, as well as support for more storage. However, with the size of processors getting larger and larger versus a standard motherboard size, there can be concessions made in I/O depending on the chassis.
The point of a dual CPU setup is not only to increase the number of ports and I/O but also to double the number of cores and separate processing power for better memory bandwidth, parallel performance, and improved multitasking. Workloads such as rendering complex 3D scenes, exporting large video files, deploying multi-instance virtual machines, training complex AI, and more can take advantage of more computing and more cores.
Dual CPU systems can deliver performance uplift over single CPU systems by sharing memory resources and splitting workloads between the two. Doubling the number of processors should effectively double the performance of a workload, right? So why isn’t everyone running a dual CPU configuration?

Does Your Workload Require 2 CPUs?
Many common workloads that day-to-day people do, like gaming, surfing the web, streaming movies, or graphic design and content creation often don’t need anything more than a single CPU. Most casual workloads cannot even take advantage of the second CPU and will actually suffer in performance. CPU 2 stands idle, consuming wattage and generating heat without doing any work, not to mention the extra cost incurred.
With the technological advances in GPU optimization and single socket CPUs like AMD Threadripper PRO and Intel Xeon W, compute intensive tasks can reach optimal performance without a second CPU counterpart. Taking GPUs out of the equation, modern CPUs now have higher core counts, thread count, cache, and computing power than ever before, replacing the dual CPU setup for a more economical single CPU configuration.
Another factor to consider is the intercommunication between two CPUs. If your workload does reach high throughput, bear in mind dual CPU servers have additional latency due to NUMA (non-uniform memory access) where the two CPUs have to communicate to share resources. NUMA is not a bottleneck, it is just the inherent design of incorporating the large number of cores across two processors. NUMA is actually quite efficient in solving this issue when sharing CPU1's share of the workload with CPU2's. However, if you can avoid the NUMA overhead, you can mitigate the latency by partitioning workloads between the two CPUs. NUMA isn't a drawback or disadvantage, just a consideration/precaution.
It is also important to consider the if dual CPU computing is supported and optimized by that workload. Some workloads won't recognize the second CPU as available resources.
If you are choosing between dual 32 core CPUs or a single 64 core CPU, it is best to stick with the single CPU configuration to avoid the dual CPU communication overhead and unknown optimization, especially when your workload isn’t partitioning compute like in virtualization and powering cloud instances.

Fueling Innovation with an Exxact Multi-GPU Server
Accelerate your workload exponentially with the right system optimized to your use case. Exxact 4U Servers are not just a high-performance computer; it is the tool for propelling your innovation to new heights.
Configure NowWhen are Dual CPU Systems Used?
As of 2024, present-day CPUs are miles ahead of what they used to be; high core counts, multi-thread capabilities, and high performance; dual CPUs are rarely at your desk, only seen in data centers.
For example, let's look at streaming games online, where a dual CPUs setup could be beneficial in theory. The gaming workload and the video/streaming workload can be partitioning between two CPUs to avoid using important computing resources for both the gameplay and the recording thus providing a higher quality stream. However, instead of investing in a dual CPU motherboard and workstation, this workload often uses a setup with two single CPU systems. The added flexibility for hardware such as dedicated beefy GPU for one system and storage controller and capture card for stream recordings in the other. Having space for each component is more important than its density here.
True dual CPU systems are reserved for HPC servers designed for the smallest footprint. A large data center infrastructure would house thousands of servers executing high-performance tasks. Deploying 5,000 machines as opposed to 10,000 can save on rack space and time spent servicing these machines.

Some use cases for dual CPU systems include:
- Scientific Simulation
- Rendering Farms for large video and 3D content
- Deep Learning AI Training & Inference
- Computer Aided Engineering (CAE)
- Finite Element Method/Analysis (FEM/FEA)
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
- Dense Storage
- Virtualization Environments
The advantage of a dual CPU system is performance density. Multi-threaded CPU-intensive applications can be executed in a breeze, even handling multiple high-capacity databases due to their sheer power. The 64-core 128-thread AMD EPYC is a multi-threaded performance king; with 2 of them in one system, their computing power is no joke.
Furthermore, data centers optimize these CPUs to perform a set of tasks at extremely high speeds with no CPU utilization wasted. For a system that fits in a single rack at the data center, nothing beats a dual CPU system that can be virtualized into two systems. These dual CPU systems effectively have two enterprise-grade single CPU systems populating only a single rack space in the data center crunching huge amounts of data and need any last drop of extreme performance they can get within a small footprint.
Dual CPU systems also enable more PCIe lanes for multiple GPUs useful for operation doing AI training, building complex algorithms, or molecular dynamics. By increasing your CPU count and PCIe lanes, you can double your GPU count and cut time spent training or running simulations.
Some workloads within the ones listed however, sometimes cannot take advantage of a dual CPU setup, or is not CPU dependent, relying on mostly the GPU. Life Science simulation programs like AMBER and GROMACS actual lose performance when ran on a dual CPU configuration and would be better off with a single processor.
Dual CPU workstation also exist. However, the space required to fit 2 modern CPUs (especially the extra-large AMD EPYC 9004) on a standard ATX or EATX motherboard can get cramped. Stuffing compute in a less dense chassis can leave additional PCIe lanes unaccounted, incur RAM limitations, and reduce number of storage bays. Dual CPU workstations are reserved for those looking for more CPU compute in a flexible workstation form factor.
How to Optimize Dual CPU System Workloads
The biggest factor when deciding on a dual CPU or single CPU solution is the workload. While Dual CPU systems can be beneficial for parallel computing (calculations performed simultaneously) like rendering, they can cause latency issues when executing tasks serially (calculations performed subsequently). While a Cinebench test (parallel) can show double the performance, a 7zip test (serial) won’t be able to take advantage of dual CPU and in some faults, be slower.
The best way to optimize dual CPUs is to separate datasets and workloads. When training a deep learning neural network for Natural Language Processing, split the preprocessing and the and training tasks to utilize both CPUs effectively. Or for your scientific research in cryo-EM 2D classification and 3D reconstruction allocate resources to the 2D classification while the rest are allocated for 3D reconstruction. Almost any HPC application can be sped up dramatically if you can parallelize the steps in a workload since the time it takes to complete 2 conjoining tasks can be faster than sequentially executing them.
Deploying a virtual machine using a hypervisor like VirtualBox or RedHat can make two separate systems for two separate purposes. Run the two datasets separately on the two VMs. Because VM1 and VM2 are independent machines operating like a single CPU system, these CPUs can work in parallel executing serial tasks.
Some research institutes will opt to configure a whole cluster and partition resources to specific steps in the research. Some compute for the molecular dynamics simulation, some for the cryo-EM machine in the lab, some for protein folding to conceptualize binding targets, you get the idea. By splitting the resources up among lower computationally expensive workloads enable efficient and consolidated workflow where all the working data is in a single place. Reducing the time to transfer data from workstation to workstation, keeping data stored in the cluster, and computing everything in parallel dramatically accelerates research and reduced the total time to completion.

So, do you need Dual CPUs?
With current-generation CPUs holding so much power, there isn’t a substantial need for a dual CPU system for mainstream consumer usage. Enthusiast AI training and deep learning workloads can benefit from parallel computing through a single CPU with multiple GPUs.
However, if your workload is on the HPC level like crunching extremely large datasets, training large AI models with the highest efficiency, or running massively compute-intensive scientific simulations, and you want to execute these tasks with the smallest footprint, deploying multiple Dual CPU configuration might be your answer.

We're Here to Deliver the Tools to Power Your Research
With access to the highest performing hardware, at Exxact, we can offer the platform optimized for your deployment, budget, and desired performance so you can make an impact with your research!
Talk to an Engineer Today
